
Product Storage
Many industries rely on cool room facilities (38° F to 40° F) for storage of perishable products. These facilities typically use chilled water or refrigeration equipment to produce the necessary cooling.
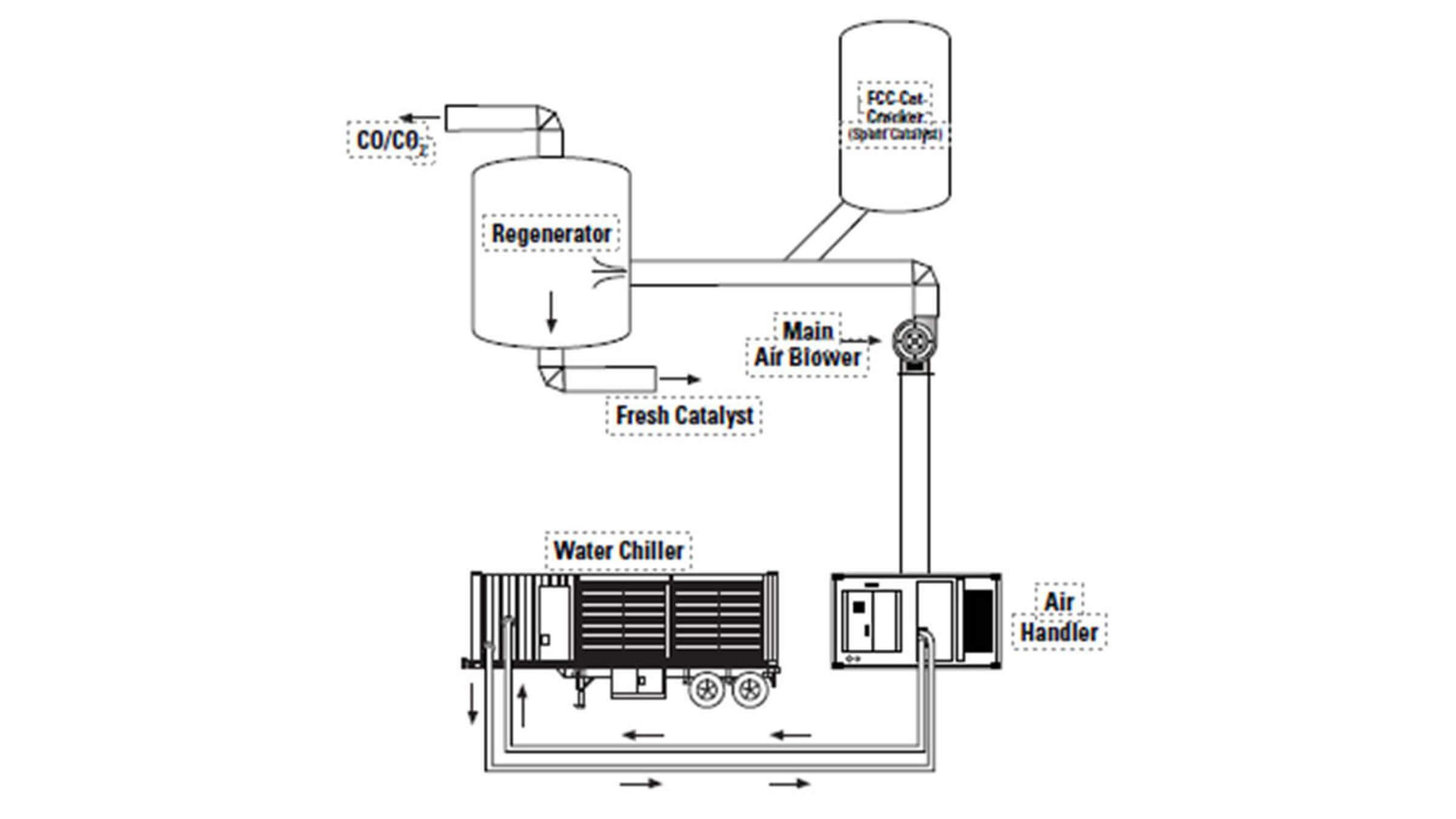
Dense Air Injection
During summer months, air is less dense, resulting in less oxygen per cubic foot of ambient air. Production rates can be maintained by chilling the air and blowing it into the process.
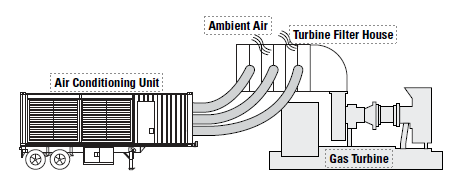
Turbine Inlet Cooling
Many industries use gas turbine engines to power a variety of compressors, generators and other equipment. These engines require large amounts of oxygen to run efficiently.

Large Motor Cooling
Production processes are sometimes limited during summer months because of overheating of large motors, transformers, motor control centers and other equipment. This is particularly true when the equipment is located in a dirty or dusty environment.

Concrete Cooling
Some concrete pours must maintain a precise temperature to achieve the specified strength and characteristics. In these cases, contractors often have to work at night, which increases their labor costs.

Cold Room Storage
Many industries rely on cool room facilities (38° F to 40° F) for storage of perishable products. These facilities typically use chilled water or refrigeration equipment to produce the necessary cooling.

Temporary Structure Cooling & Heating
Special events such as trade shows, conferences and concerts are often held in large temporary structures or tents. Depending on location and the type of event, heating and cooling may be required for these structures. Most event planners rely on rental systems for these needs.

