
Product Storage
Many industries rely on cool room facilities (38° F to 40° F) for storage of perishable products. These facilities typically use chilled water or refrigeration equipment to produce the necessary cooling.
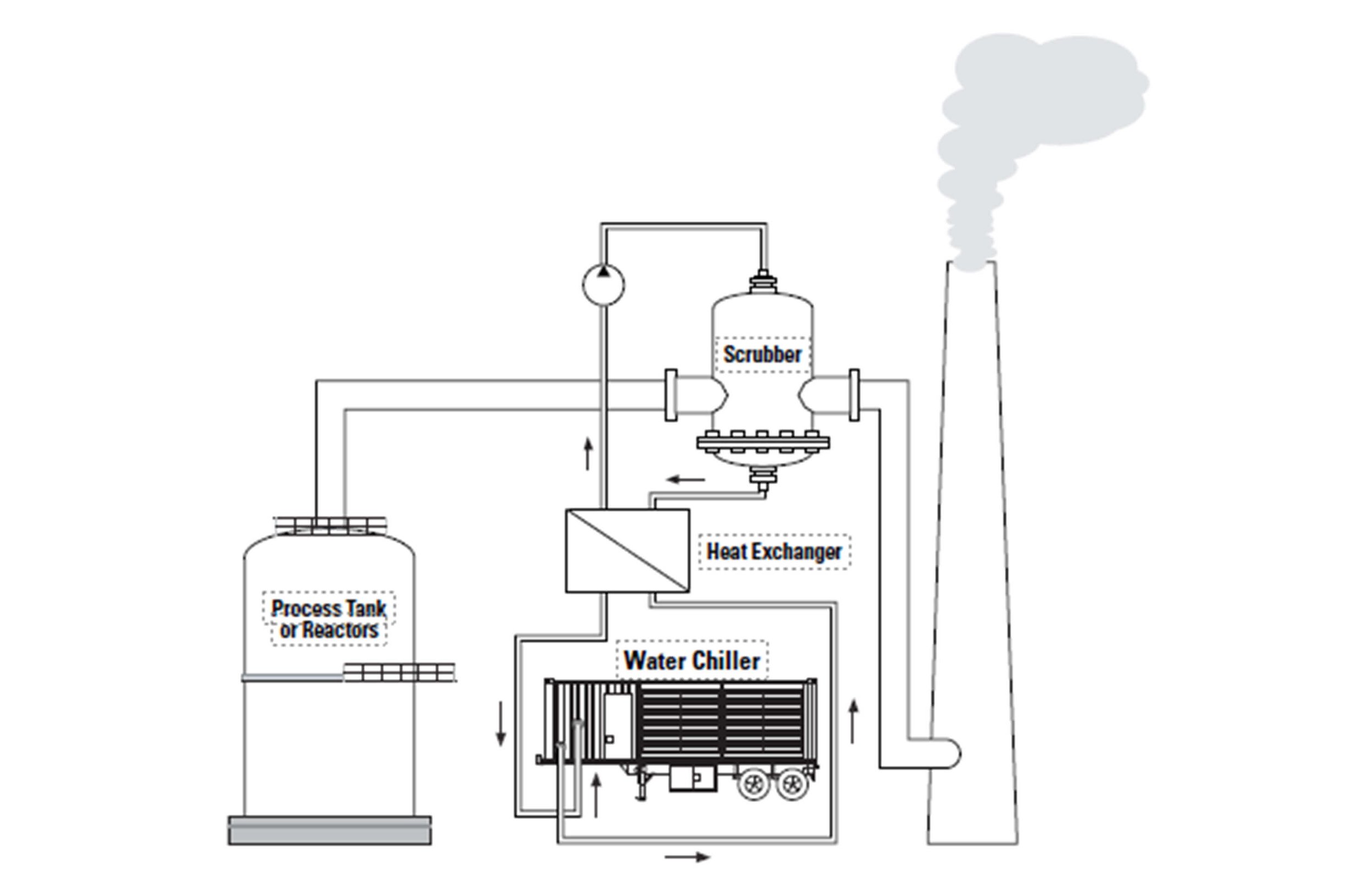
Scrubber Cooling
Scrubbers use a solution to remove chemicals from gases within a tank. A scrubber must be cooled to maintain low emission and high production levels.

Plastics Production Processes
Many different processes within the plastics industry rely on a continual supply of chilled water.
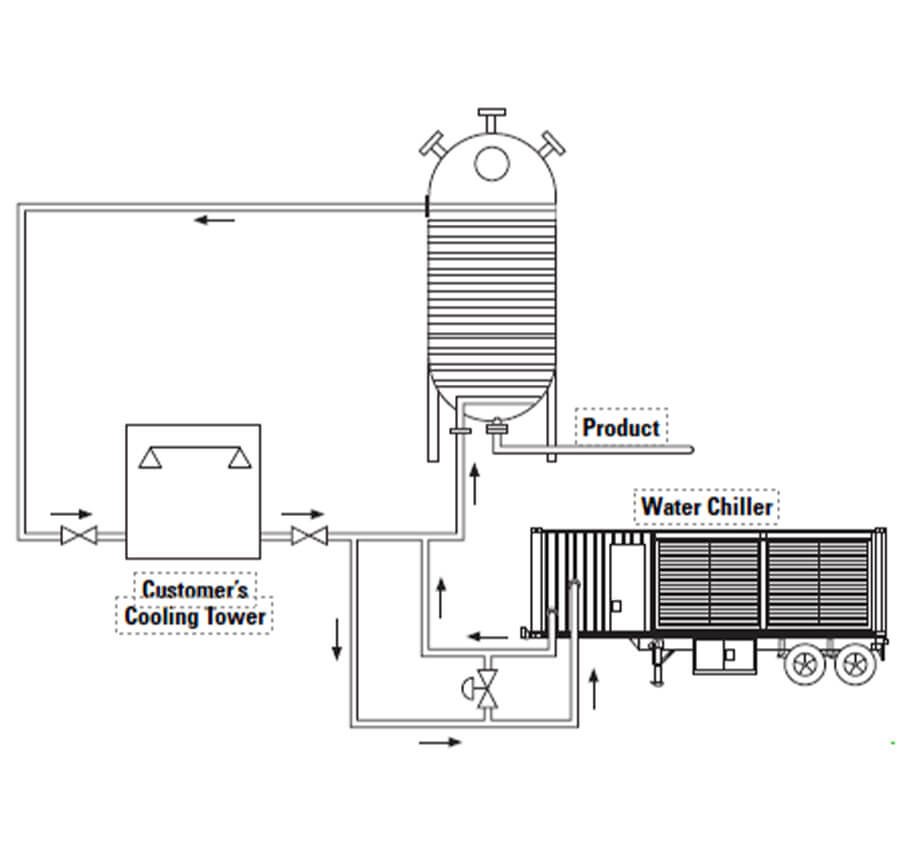
Jacketed Reactor Cooling
Companies that produce chemicals or pharmaceuticals use reactors. Water or brine is usually circulated through the reactor jacket or coils to control the heat of the reaction. Without sufficient cooling, reactor operations might have to be shut down.
Dense Air Injection
During summer months, air is less dense, resulting in less oxygen per cubic foot of ambient air. Production rates can be maintained by chilling the air and blowing it into the process.
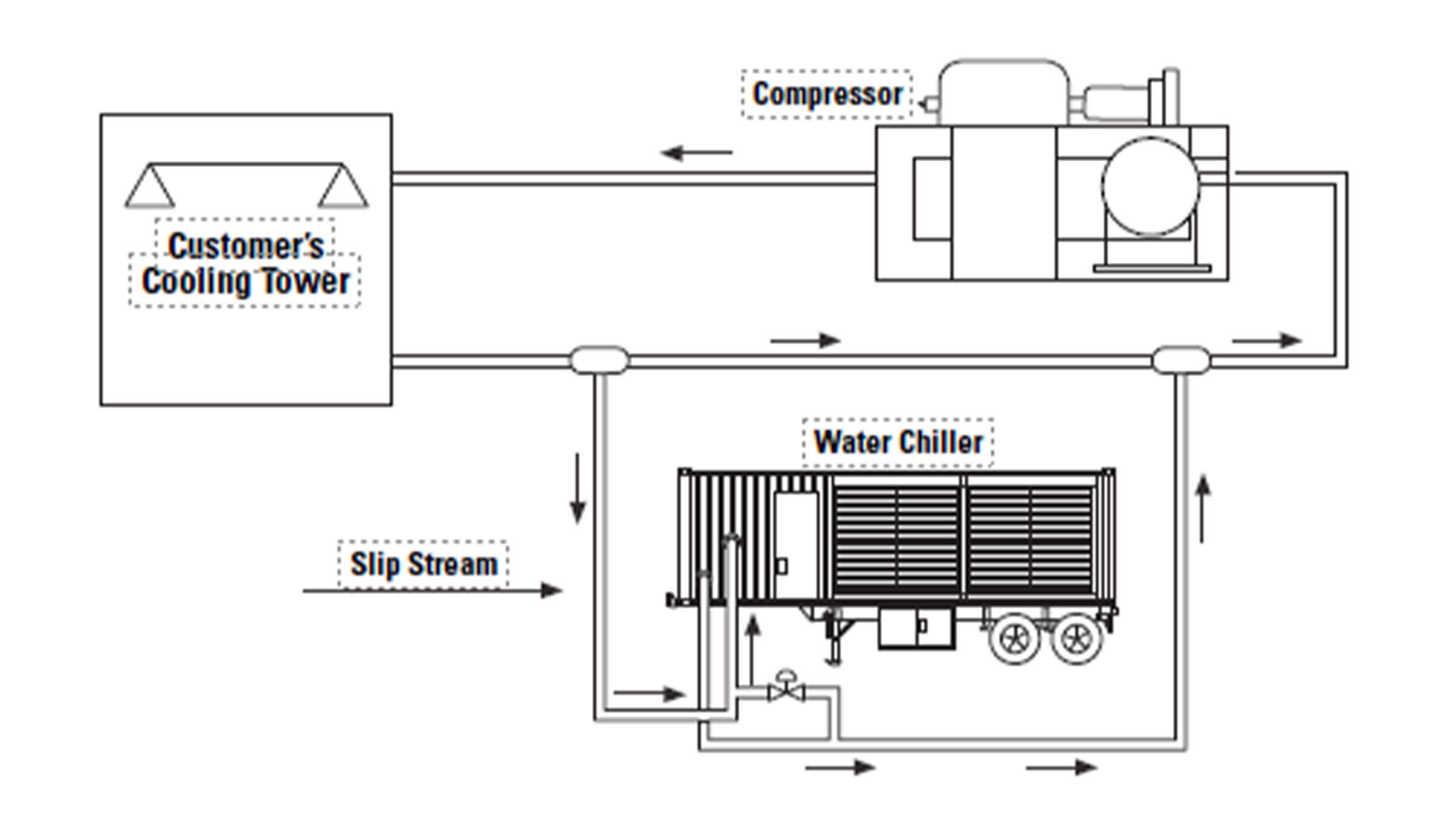
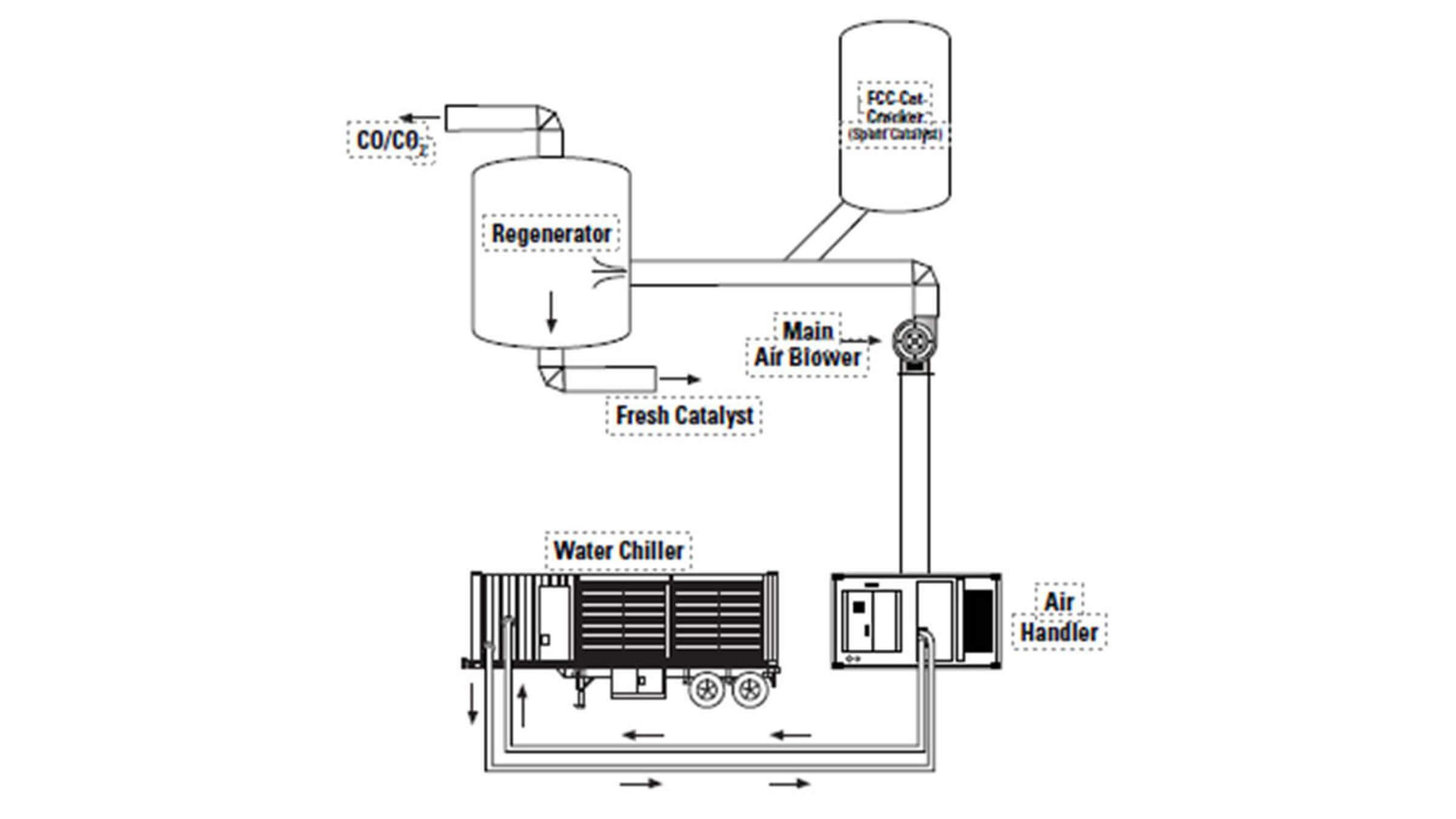
Wet Gas Compressor Cooling
Wet gas compressors compress light gases such as butane and propane and deliver them to a cat cracker as a portion of the feed to a reaction chamber. Many of these compressors are cooled using a water jacket and cooling tower water.
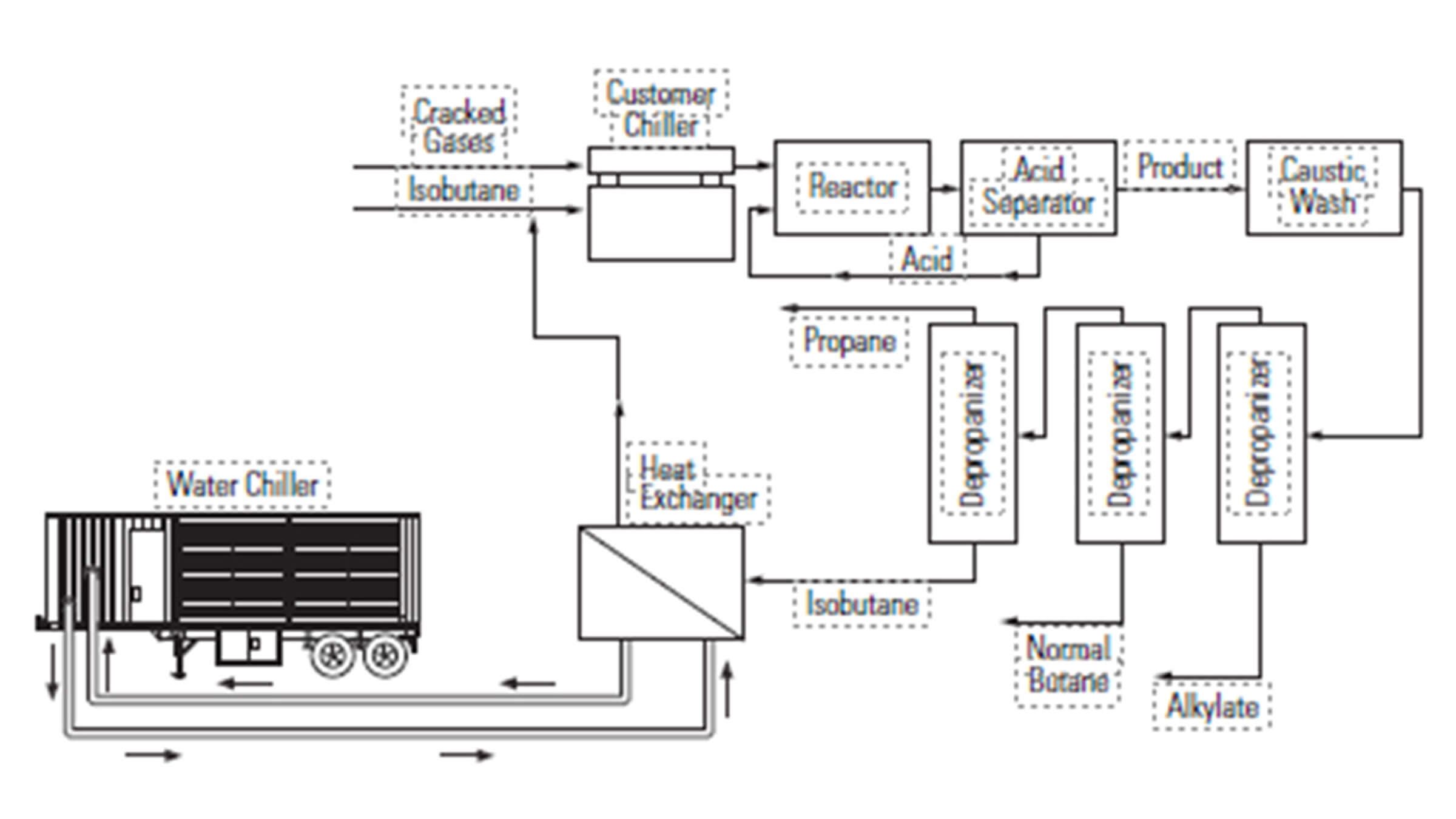
Alkylation (Alky) Cooling
Oil refineries employ chemical reaction processes to produce alkylate, a product that is blended with gasoline to increase its octane rating and lower its vapor pressure.
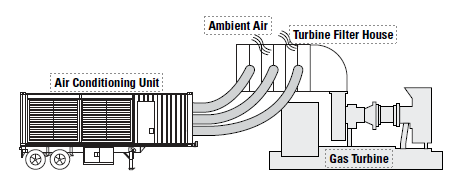
Turbine Inlet Cooling
Many industries use gas turbine engines to power a variety of compressors, generators and other equipment. These engines require large amounts of oxygen to run efficiently.

Large Motor Cooling
Production processes are sometimes limited during summer months because of overheating of large motors, transformers, motor control centers and other equipment. This is particularly true when the equipment is located in a dirty or dusty environment.
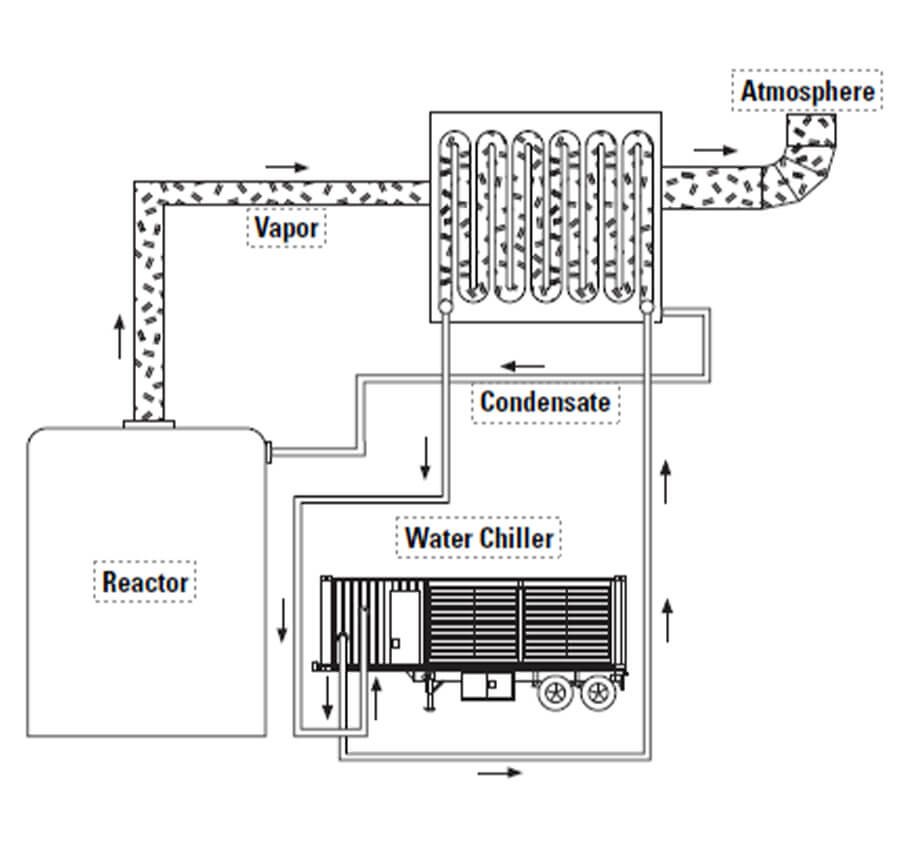
Condenser Cooling
During summer months, the existing cooling equipment is stressed and may not keep up with demand, requiring cutbacks in production. Rental chillers can provide both backup and supplemental cooling capacity. The drawing below shows one possible installation.

Waste Water Treatment
A widely used method of treating wastewater is through treatment ponds, where bacteria break down the waste materials. These microorganisms are heat sensitive and die if the pond gets too hot.
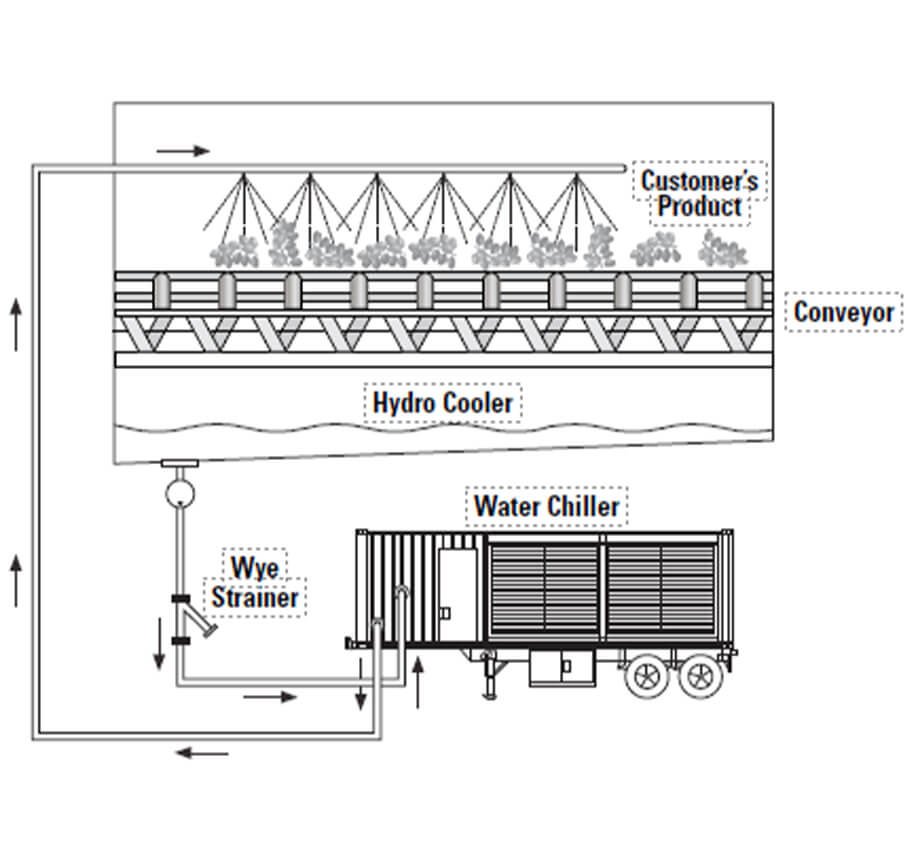
Food Products Cooling and Quenching
Because of the seasonal nature of harvesting, many companies may find it more economical to rent chillers, rather than owning permanent systems.

Ice Rink Cooling
Rental systems are always a first choice in the event of permanent equipment failure at ice rinks. Rental chillers are also ideal for temporary and seasonal rinks—which are becoming more common—as they do not require a large capital investment.

Concrete Cooling
Some concrete pours must maintain a precise temperature to achieve the specified strength and characteristics. In these cases, contractors often have to work at night, which increases their labor costs.
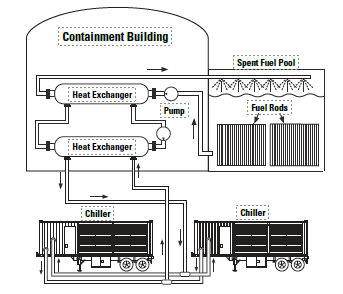
Containment & Spent Fuel Pool Cooling
Nuclear reactors use highly radioactive materials to produce great amounts of heat. These processes are housed in containment buildings that must have a constant supply of chilled water and air. The byproduct of the reactor is spent fuel that remains radioactive and must be constantly cooled in a pond or tank.

Vapor Recovery and Liquefied Gas Storage
Liquefied gasses such as butane, propane, natural gas and others are condensed and stored in large pressurized tanks. A portion of this liquefied gas boils off as vapor, both during production and storage and must be re-condensed and returned to the storage tank.

Supplemental Cooling Tower Water
Rental chillers are the ideal solution to supplement cooling tower capacity and lower water temperature sufficient to support production processes.

Cold Room Storage
Many industries rely on cool room facilities (38° F to 40° F) for storage of perishable products. These facilities typically use chilled water or refrigeration equipment to produce the necessary cooling.

Temporary Structure Cooling & Heating
Special events such as trade shows, conferences and concerts are often held in large temporary structures or tents. Depending on location and the type of event, heating and cooling may be required for these structures. Most event planners rely on rental systems for these needs.
Environmental Control (heating/cooling/dehumidification)
Temporary heating, air conditioning or dehumidification packages are occasionally needed to replace permanent systems during maintenance, repair, or replacement and to supplement permanent system capacity.

